AWS Well-Architected Framework: Complete Guide to the 6 Pillars
AWS Well-Architected Framework: Complete Guide to the 6 Pillars
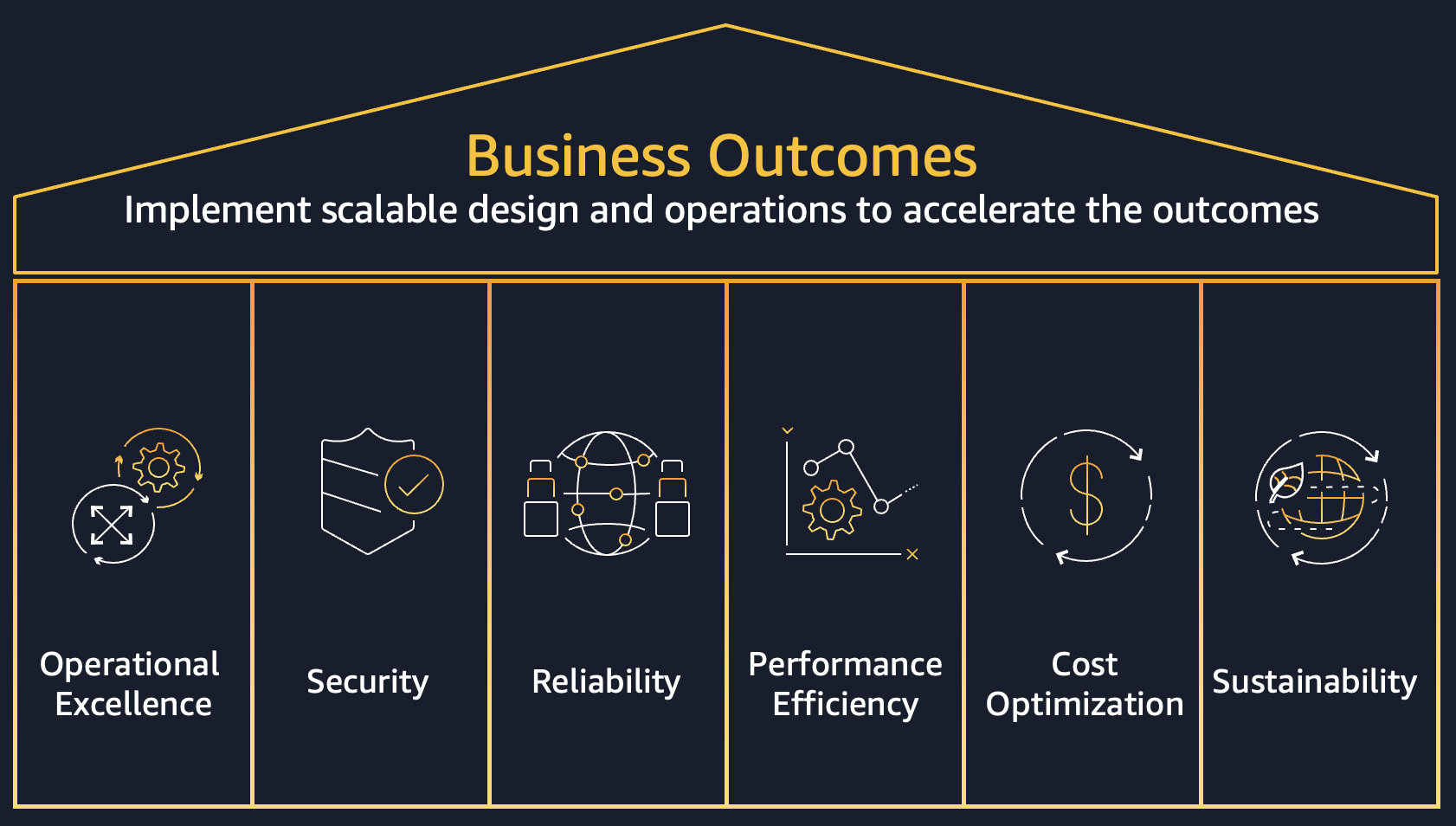 Building robust cloud applications on AWS requires more than just technical skills—it demands a structured approach to architecture. The AWS Well-Architected Framework provides exactly that: a comprehensive set of best practices organized into six fundamental pillars that ensure your cloud solutions are secure, reliable, and cost-effective.
Building robust cloud applications on AWS requires more than just technical skills—it demands a structured approach to architecture. The AWS Well-Architected Framework provides exactly that: a comprehensive set of best practices organized into six fundamental pillars that ensure your cloud solutions are secure, reliable, and cost-effective.
Think of these pillars as the foundation of a building. Just as a structure needs a solid foundation to remain stable, your AWS architecture needs these six pillars to deliver consistent performance and meet business requirements.
What is the AWS Well-Architected Framework?
The AWS Well-Architected Framework is a set of guiding principles and best practices that help cloud architects build secure, high-performing, resilient, and efficient infrastructure for applications and workloads. Originally consisting of five pillars, AWS added Sustainability as the sixth pillar in 2021, reflecting the growing importance of environmental responsibility in cloud computing.
The 6 Pillars of AWS Well-Architected Framework
1. Operational Excellence
Focus: Running and monitoring systems to deliver business value and continually improve processes.
Operational Excellence is about building software correctly while consistently delivering exceptional customer experiences. This pillar emphasizes the importance of understanding your workloads, implementing effective monitoring, and creating processes that support continuous improvement.
Key Principles:
- Perform operations as code: Treat your infrastructure and operations procedures as code that can be versioned, tested, and deployed
- Make frequent, small, reversible changes: Implement changes incrementally to reduce risk and enable quick rollbacks
- Refine operations procedures frequently: Continuously improve your operational processes based on lessons learned
- Anticipate failure: Design systems that can handle failures gracefully and learn from incidents
- Learn from operational failures: Use failures as opportunities to improve your systems and processes
Best Practices:
- Implement Infrastructure as Code (IaC) using AWS CloudFormation or Terraform
- Use AWS Systems Manager for patch management and configuration
- Set up comprehensive monitoring with Amazon CloudWatch
- Implement automated incident response procedures
- Conduct regular operational reviews and post-incident analyses
2. Security
Focus: Protecting information, systems, and assets while delivering business value through risk assessments and mitigation strategies.
Security in the cloud is a shared responsibility between AWS and you. This pillar ensures that your applications and data are protected through multiple layers of security controls, from network security to data encryption.
Key Principles:
- Implement a strong identity foundation: Use centralized identity management and eliminate long-term credentials
- Apply security at all layers: Implement defense in depth with multiple security controls
- Enable traceability: Monitor and log all actions and changes in your environment
- Automate security best practices: Use automation to implement security controls consistently
- Protect data in transit and at rest: Encrypt sensitive data using appropriate encryption methods
- Keep people away from data: Minimize direct access to data and use automated tools instead
- Prepare for security events: Have incident response procedures and practice them regularly
Best Practices:
- Use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) with least privilege principles
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users
- Encrypt data using AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
- Use AWS Security Hub for centralized security monitoring
- Implement network security with VPCs, security groups, and NACLs
- Regular security assessments and penetration testing
3. Reliability
Focus: Ensuring a workload performs its intended function correctly and consistently when expected.
Reliability is about building systems that can recover from failures and meet business and customer demand. This pillar focuses on designing resilient architectures that can handle component failures, traffic spikes, and other disruptions.
Key Principles:
- Automatically recover from failure: Monitor systems and trigger automated recovery when thresholds are breached
- Test recovery procedures: Regularly test how your system fails and validate recovery procedures
- Scale horizontally: Distribute workload across multiple smaller resources to reduce single points of failure
- Stop guessing capacity: Use auto-scaling and monitoring to match capacity with demand
- Manage change through automation: Use automation to make changes to infrastructure and reduce human error
Best Practices:
- Design for failure by implementing redundancy across multiple Availability Zones
- Use Auto Scaling Groups to handle varying loads automatically
- Implement health checks and automated failover mechanisms
- Use Amazon RDS Multi-AZ deployments for database reliability
- Implement circuit breakers and retry logic in applications
- Regular disaster recovery testing and backup validation
4. Performance Efficiency
Focus: Using IT and computing resources efficiently to meet system requirements and maintain efficiency as demand changes.
Performance Efficiency is about selecting the right resource types and sizes based on workload requirements, monitoring performance, and making informed decisions to maintain efficiency as business needs evolve.
Key Principles:
- Democratize advanced technologies: Use managed services to reduce operational burden
- Go global in minutes: Deploy systems in multiple regions to reduce latency
- Use serverless architectures: Eliminate the need to manage servers
- Experiment more often: Use virtual resources to test different configurations
- Consider mechanical sympathy: Understand how cloud services work and choose accordingly
Best Practices:
- Choose the right compute services (EC2, Lambda, Fargate) based on workload characteristics
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDN) like Amazon CloudFront for global content delivery
- Implement caching strategies with Amazon ElastiCache
- Use Amazon RDS Performance Insights for database optimization
- Monitor performance metrics and set up automated scaling
- Regular performance testing and optimization
5. Cost Optimization
Focus: Running systems to deliver business value at the lowest price point while meeting requirements.
Cost Optimization is about understanding and controlling where money is being spent, selecting appropriate resource types, analyzing spend over time, and scaling to meet business needs without overspending.
Key Principles:
- Implement cloud financial management: Establish cost awareness and accountability
- Adopt a consumption model: Pay only for what you use
- Measure overall efficiency: Monitor business output and costs associated with delivering it
- Stop spending money on undifferentiated heavy lifting: Use managed services to reduce operational costs
- Analyze and attribute expenditure: Understand how costs are distributed across your organization
Best Practices:
- Use AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets for cost monitoring
- Implement Reserved Instances and Savings Plans for predictable workloads
- Use Spot Instances for fault-tolerant workloads
- Right-size resources based on actual usage patterns
- Implement automated resource scheduling for non-production environments
- Regular cost reviews and optimization recommendations
6. Sustainability
Focus: Minimizing the environmental impacts of running cloud workloads through energy-efficient practices.
Sustainability is the newest pillar, added in 2021, focusing on environmental impacts of cloud workloads. This pillar helps organizations understand the environmental impact of their cloud usage and implement strategies to reduce their carbon footprint.
Key Principles:
- Understand your impact: Measure and monitor the environmental impact of your workloads
- Establish sustainability goals: Set long-term sustainability goals for your workloads
- Maximize utilization: Right-size workloads and implement efficient design patterns
- Anticipate and adopt new, more efficient hardware and software offerings: Stay current with AWS innovations
- Use managed services: Reduce the environmental impact of maintaining infrastructure
- Reduce the downstream impact: Minimize the amount of energy or resources required to use your services
Best Practices:
- Use AWS regions powered by renewable energy
- Implement efficient coding practices to reduce compute requirements
- Use serverless and managed services to improve resource utilization
- Optimize data storage and transfer to reduce energy consumption
- Monitor and report on sustainability metrics
- Choose instance types with better performance per watt
Implementing the Well-Architected Framework
Getting Started
- Assessment: Use the AWS Well-Architected Tool to assess your current architecture
- Prioritization: Identify high-risk issues and prioritize improvements
- Implementation: Apply best practices systematically across all pillars
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor and measure improvements
- Iteration: Regularly review and update your architecture
Tools and Resources
- AWS Well-Architected Tool: Free service for reviewing your architectures
- AWS Trusted Advisor: Provides recommendations across all pillars
- AWS Config: Monitors compliance with best practices
- AWS CloudFormation: Infrastructure as Code for consistent deployments
- AWS Well-Architected Labs: Hands-on labs for each pillar
Real-World Application Example
Consider an e-commerce application built on AWS:
- Operational Excellence: Use CI/CD pipelines with AWS CodePipeline, monitor with CloudWatch
- Security: Implement WAF, encrypt data with KMS, use IAM roles
- Reliability: Deploy across multiple AZs, use RDS Multi-AZ, implement auto-scaling
- Performance: Use CloudFront CDN, ElastiCache for caching, optimize database queries
- Cost Optimization: Use Reserved Instances for baseline capacity, Spot Instances for batch processing
- Sustainability: Choose energy-efficient instance types, optimize code for better performance per watt
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Focusing on only one pillar: All six pillars are interconnected and equally important
- One-time assessment: Architecture review should be an ongoing process
- Ignoring trade-offs: Sometimes optimizing for one pillar may impact another
- Over-engineering: Apply practices proportional to your business requirements
- Lack of measurement: Without metrics, you can’t validate improvements
Conclusion
The AWS Well-Architected Framework’s six pillars provide a comprehensive approach to building robust, secure, and efficient cloud applications. By systematically applying these principles, you can create architectures that not only meet current requirements but also adapt to future needs.
Remember, well-architected systems are not built overnight. Start with an assessment, prioritize improvements based on business impact, and continuously iterate. The framework is not a one-size-fits-all solution but rather a set of guiding principles that should be adapted to your specific use case and requirements.
Whether you’re migrating existing applications to AWS or building new cloud-native solutions, the Well-Architected Framework serves as your roadmap to success. By embracing all six pillars—Operational Excellence, Security, Reliability, Performance Efficiency, Cost Optimization, and Sustainability—you’ll build systems that deliver exceptional business value while minimizing risks and costs.
Next Steps
- Take the Assessment: Use the AWS Well-Architected Tool to evaluate your current architecture
- Create an Action Plan: Prioritize improvements based on your assessment results
- Start Small: Begin with quick wins that provide immediate value
- Measure Progress: Track improvements using relevant metrics for each pillar
- Stay Updated: AWS continuously updates best practices, so keep learning and adapting
The journey to a well-architected system is ongoing, but with these six pillars as your foundation, you’re well-equipped to build cloud solutions that stand the test of time.